
Sun and baby skin
Special protection for your baby
Baby skin is five times thinner than that of adults, and therefore much more sensitive. This is why children need special protection from the sun.
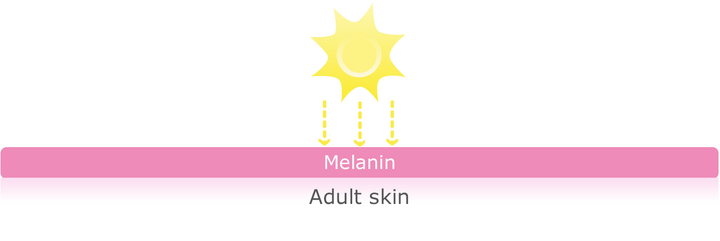
Melanin is the term used to describe the brown coloured pigments that the sun can cause to produce on the skin (tanning of the skin). These brown coloured pigments absorb incoming UV rays, converting them into heat, thereby protecting the skin. The protection depends on the intensity of the UV radiation and the duration of exposure. The low melanin content in a baby’s skin means, among other things, that their skin burns very quickly. Because of the low level of natural sun protection (due to the low melanin content), a baby’s sensitive skin must be particularly well protected from the sun.
Melanin is responsible for the colour of our skin, hair, and eyes. It is also responsible for the tanning of the skin. During sun exposure, these pigments absorb1 the light and are thereby able to protect the skin for a certain amount of time, depending on the intensity of the UV radiation.
1 The brown colour pigments absorb the UV rays and convert them into heat, thereby protecting the skin.
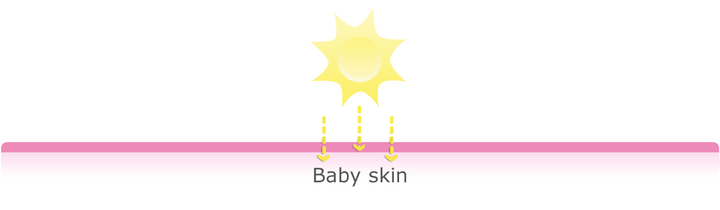
As is the case with very fair-skinned adults, baby skin produces very low levels of melanin, which is why their skin burns very quickly.
This low melanin content means that baby skin has a low level of natural sun protection, making it all the more important to protect babies’ sensitive skin from the sun.